EnArBgDeElEsFaFiFrHiHuItJaKnKoMsNlPlPtRuSqThTrUkZh
Windows does not have ssh daemon As i read you want to login in your windows machine. QNX side: inetd + sshd is only if you want to use e.g. Putty on windows and connect to your QNX machine. QNX (/ ˌ k juː ˌ ɛ n ˈ ɛ k s / or / ˈ k juː n ɪ k s /) is a commercial Unix-like real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market. QNX was one of the first commercially successful microkernel operating systems. citation needed As of 2020.
- 3Setup your Qt Creator environment
- 4Compile and Deploy
Overview
The QNX plugin is available in Qt Creator since the version 2.6. It provides support for application development for BlackBerry 10 smartphones as well as for QNX Neutrino OS on embedded devices.
You can download a recent Qt Creator release version via this link.
The QNX plugin is under constant development. Many improvements and bug fixes did not make into the recently released 3.1 version. If you want to try a cutting-edge Qt Creator build that contains latest features and bug fixes in the QNX plugin, you can consider downloading a snapshot build via this link.
A few generic topics on this page overlap with the Qt application development and deployment on QNX page which focuses on the command line use case.
Note: The steps described in this page cover Qt Creator 3.1 feature level. If you are using a previous version, some steps might need to be done slightly different.
Getting Started
The following tools are required for development for the QNX platform using Qt Creator:
- Qt build for QNX installed on your target and on your development machine
- Qt Creator 3.1 (most steps should be valid for the version 2.6 and later as well)
- QNX Software Development Platform (SDP) 6.6 (most steps should be valid for SDP 6.5 FP1 as well)
- QNX SDK for Apps and Media 1.0 if you use SDP 6.6. This is an optional package providing additional BlackBerry tools for easy deployment and installation of applications on a target.
Setup your Qt Creator environment
You first have to manually add your Qt for QNX as a new Qt version, configure the compiler, the debugger and create the kit. In the future Qt Creator releases, QNX plugin should be able to automatically setup all these tools by just selecting the path to the installed QNX SDP.
Add the Qt version
You add the Qt version by selecting Tools -> Options-> Build & Run > Qt Versions -> Add and set the path to 'qmake' in your Qt for QNX build. You also need to specify a path to the QNX SDP installation to let Qt Creator to validate the newly added Qt version: Streaming clients for mac.
This won't be required in the future releases of Qt Creator. If you are using a Qt for QNX installer with integrated Qt Creator build, the new Qt version for QNX will be detected automatically and added to this Qt Creator installation.
Add the QCC compiler
Select Tools -> Options-> Build & Run -> Compiler-> Add -> QCC and set the path to the qcc compiler (<qnx660_path>/host/<OS>/x86/usr/bin/qcc). Since qcc depends on some QNX specific environment variables, you need to specify the path to the QNX SDP installation as well:
Add a debugger
Select Tools -> Options-> Run & Build -> Debugger and set the path to the ntoarmv7-gdb debugger (<qnx660_path>/host/<OS>/x86/usr/bin/ntoarmv7-gdb) or ntox86-gdb if you're targeting x86:
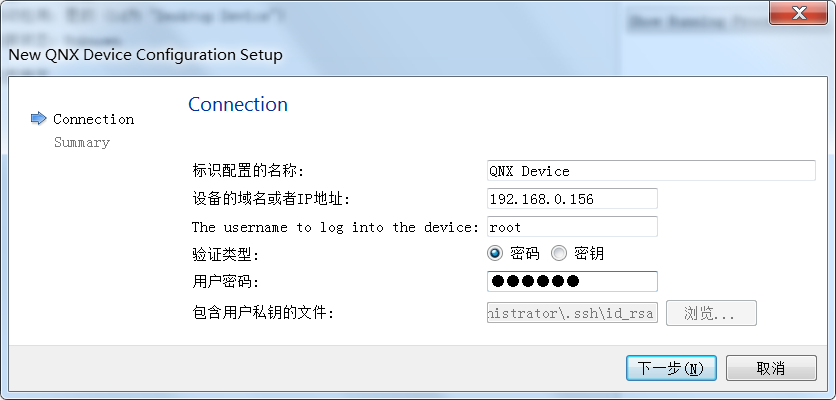
Add QNX Device
Select Tools -> Options-> Devices -> Add-> QNX Device to register your QNX device in Qt Creator.
Add a kit
Select Tools -> Options-> Build & Run -> Kits-> Add to add a new kit that uses the QNX device, the Qt version , the compiler and the debugger your setup during the steps above:
Compile and Deploy
Compiling and deploying applications for QNX is very similar to how it is done for 'Remote Linux' devices, see the Qt Creator manual for more information via this link.
Pointing to the Qt runtime on the target
When running the application on the QNX device, you might need to specify the path to where the Qt runtime is installed on the device. This is done in the 'Run Settings' of your project in Qt Creator. The application will not start if this is not done, check the logs to find out if this is the case.
A Qt application can be pointed to the location of the Qt runtime by a few environment variables. Set the following environment variables:
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/<qt_installation_path>/libQML_IMPORT_PATH= /<qt_installation_path>/importsQML2_IMPORT_PATH= /<qt_installation_path>/qmlQT_PLUGIN_PATH=/<qt_installation_path>/pluginsQQNX_PHYSICAL_SCREEN_SIZE='150,90'
Note: If your target already uses some of those variables system-wide, make sure if append or prepend the new values
The QQNX_PHYSICAL_SCREEN_SIZE environment variable is QNX specific and defines the height and width of the app's display area on the screen in millimeters:
If your build does not use fontconfig you also need to point where to find the Qt fonts:export QT_QPA_FONTDIR=/<qt_installation_path>/lib/fonts
Application deployment
The simplest way to deploy an app on a target is to copy its binaries into a remote folder. Qt Creator does all this for your. Vst colossus for mac. You just need to make sure that the destination folder is correct and is writable.
If your .pro file does not already contain specific deployment instructions for the QNX platform or contains instructions specific for another platform, make sure a valid target path is set as following:
- /tmp is mapped to a RAM drive on many devices. This means your app will be deleted after the next reboot.
qnx {
}
Note: Most Qt examples already contain deployment instructions in their .pro files, e.g.:
target.path = $$[QT_INSTALL_EXAMPLES]/quick/example_xyz
Put the above 'qnx' instructions below such a line.
Tools provided by the QNX SDK
If you use QNX SDK for Apps and Media, you can use the additional BlackBerry tools to package your application as a BAR file. This is pretty similar to the packaging of BlackBerry 10 applications. See this article in the QNX developer documentation for more details.
The installation of the application packaged in a BAR file on the target is explained in this article.
Using CMake build system
Qt Creator provides a CMake plugin to manage CMake based projects. The plugin is currently not fully functional when you want to deploy and run your application on remote targets in general by default. If you develop for QNX using CMake and Qt Creator please follow the below instructions to fix this.
- When you create a new CMake project using the Qt Creator, the CMake wizard won't provide any CMake generator for QNX kits. This is a known issue in QtCreator 3.1 that should be fixed in the 3.1.1 patch release. Please download a recent 3.1.1 snapshot build here to skip this issue.
- The default CMakeList.txt file generated by Qt Creator in the root folder of your CMake project doesn't cover the QNX platform. You either have to use an appropriate cmake toolchain file for QNX or add the following configuration lines in CMakeList.txt specifying QNX SDP 6.6 toolchain:
SET (CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME QNX)SET (CMAKE_SYSTEM_VERSION 6.6.0)SET (CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR armv7) # or SET (CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR x86)SET (TOOLCHAIN QNX)
IF (CMAKE_HOST_WIN32)
ENDIF (CMAKE_HOST_WIN32)
Qnx Ssh Password
FIND_PATH(QNX_HOST
)
FIND_PATH(QNX_TARGET
)
SET (CMAKE_C_COMPILER ${QNX_HOST}/usr/bin/nto${CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR}-gcc${HOST_EXECUTABLE_SUFFIX})SET (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER ${QNX_HOST}/usr/bin/nto${CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR}-c++${HOST_EXECUTABLE_SUFFIX})
- In order to deploy the application binary into your QNX target with QtCreator, you should add a QtCreatorDeployment.txt file in the root directory of your CMake project and specify the location where your binary should de deployed, e.g.:
/account/devuser/me/myApp
or another writable folder on your target.
Note: If your need to deploy additional files, your should specify them as well in the QtCreatorDeployment.txt as explained in the documentation.
- The CMake plugin in Qt Creator does not support running remote executables yet, and the run configuration provides only the option to run a local executable. Thus, you need to manually add the necessary steps to run a custom executable on the target via ssh. For a QNX project, you can simply add a new Run custom remote command deploy step and specify the path to your executable in the target machine to run it during the deployment step.
Description:
Qnx Ssh Server
The sshd (OpenSSH Daemon) is the daemon program for ssh.Together, these programs replacerloginandrsh,and provide secure encrypted communications between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network.For more information, seesshdin the NetBSD documentation.
Setting up SSH access to a QNX Neutrino target
Here's how you can enable access via SSH and SFTP on a'plain' system that doesn't have telnet or similar configured.A writable POSIX filesystem is a requirement(fs-qnx4.so,fs-qnx6,devf*,orfs-etfs*),and it must be mounted under /.
- Add the following lines to your mkifs buildfile (if they aren't there already):
- In the boot script, start random before you launch io-pkt:
- In the library section (before [data=c]):
- In the binary section (after [data=c]):
You can also define your own versions of /etc/services and etc/ssh/sshd_config if the default versions aren't suitable.
- Generate a new OS image.
- Boot your QNX Neutrino target with the new boot image, and then do the following:
- If they don't already exist, create a writeable /etc directory for /etc/passwd, and /etc/ssh/ for the keys to be generated:
- Make sure that /etc/passwd exists and contains an entry for root (so you can create keys), and an entry for the privilege separation user, sshd:
- Generate the authentication keys. For example:
- Create the required directories:
- Start sshd:
Qnx Ssh
You should now be able to access the target with an SSH client and via SFTP.